Pluto is not a planet because it does not meet the three criteria that the International Astronomical Union (IAU) uses to define a planet. These criteria are:
- The object must be in orbit around the Sun.
- The object must be massive enough for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydro-static equilibrium (nearly round) shape.
- The object must have cleared the neighborhood around its orbit.
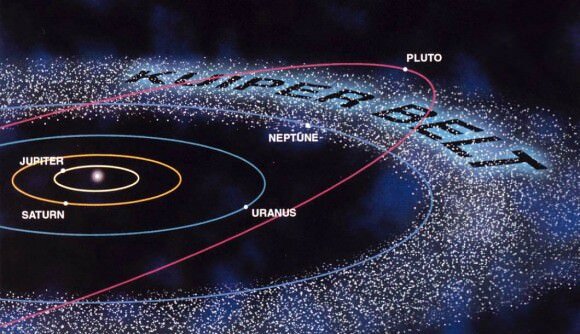
Pluto meets the first two criteria, but it does not meet the third criterion. The region of space around Pluto’s orbit is still home to many other objects, such as the Kuiper Belt objects. This means that Pluto has not cleared its neighborhood of other objects.
The demotion of Pluto to a dwarf planet was a controversial decision, and there are still many people who believe that Pluto should be considered a planet. However, the IAU’s definition of a planet is now the accepted definition, and Pluto is no longer considered a planet.
In addition to Pluto, there are five other dwarf planets in the solar system: Ceres, Eris, Haumea, Makemake, and 2007 OR10. These objects are all similar to Pluto in that they are not massive enough to have cleared the neighborhood around their orbits.
Fascinating fact about pluto
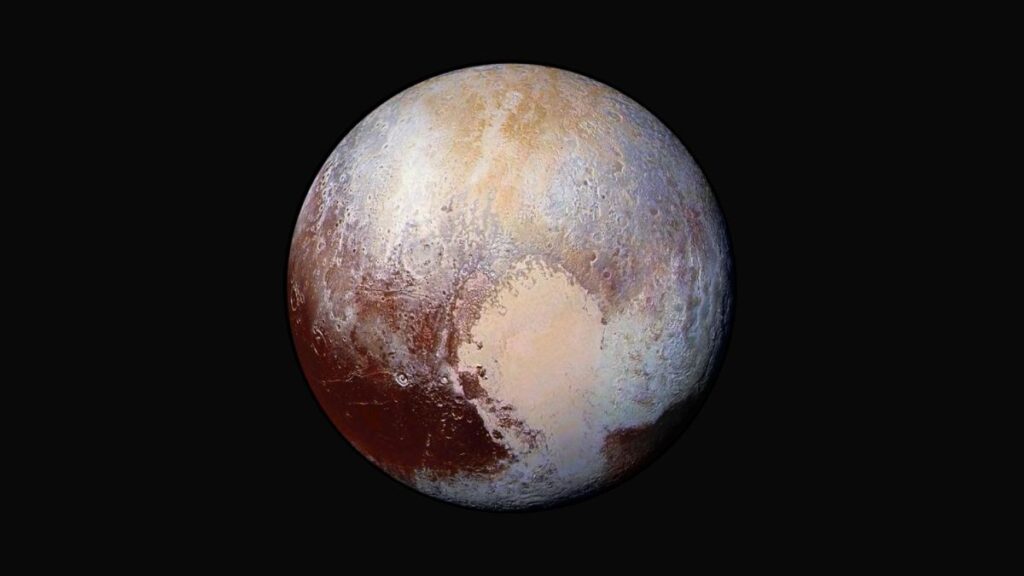
One fascinating fact about Pluto is that it has a heart-shaped feature on its surface called the “Tombaugh Regio.” This heart-shaped region was discovered by NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft during its flyby of Pluto in 2015. The Tombaugh Regio is named after Clyde Tombaugh, the astronomer who discovered Pluto in 1930.
The heart-shaped feature spans over 1,000 miles (1,600 kilometers) across and is composed of two distinct regions: a large, pale-colored region named “Tombaugh Terra” and a smaller, darker region named “Sputnik Planitia.” The Sputnik Planitia is an icy plain and is believed to be a basin filled with nitrogen ice.
The discovery of this heart-shaped feature on Pluto’s surface captured the public’s imagination and added to the intrigue surrounding the dwarf planet. It showcased the diverse and geologically active nature of Pluto, challenging the notion that it is a cold, dead world. The New Horizons mission provided valuable insights into the geology, atmosphere, and composition of Pluto, expanding our knowledge of this distant and enigmatic world in our solar system.
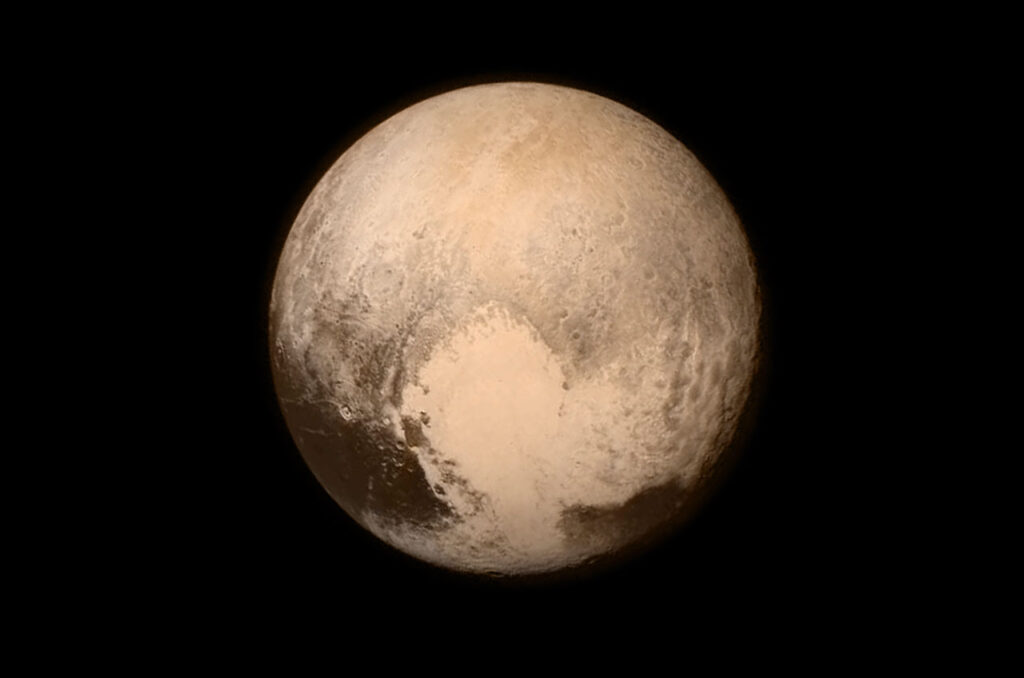

- Pluto is the ninth largest object in the solar system.
- Pluto has a very thin atmosphere made up of nitrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide.
- Pluto has five moons: Charon, Nix, Hydra, Kerberos, and Styx.
- Charon is the largest moon of Pluto and is about half the size of Pluto itself.
- Pluto’s surface is covered in craters, mountains, and valleys.
- Pluto has a heart-shaped region on its surface.
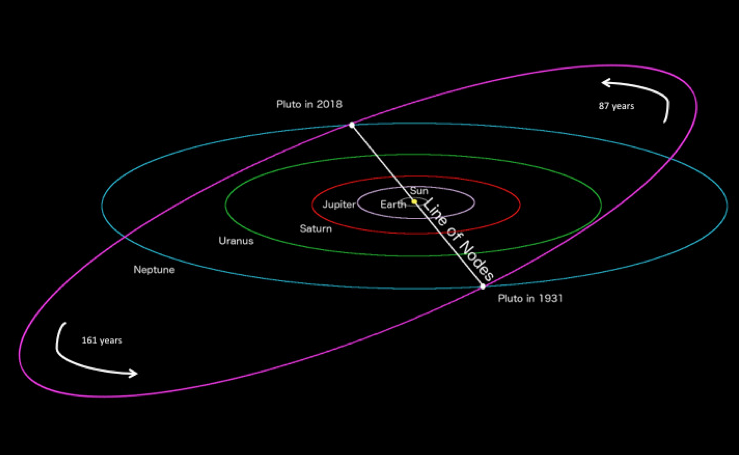
- Pluto’s orbit is very elliptical, and it sometimes comes closer to the Sun than Neptune does.
- Pluto was discovered in 1930 and was considered a planet until 2006, when it was reclassified as a dwarf planet.
Pluto is a fascinating object, and scientists are still learning about it. The New Horizons spacecraft flew by Pluto in 2015, and the data it collected has helped scientists to learn more about this dwarf planet.