James Edwin Webb (October 7, 1906 – March 27, 1992) was an American government official who served as Undersecretary of State from 1949 to 1952. He was the second Administrator of NASA from February 14, 1961, to October 7, 1968. Webb led NASA from the beginning of the Kennedy administration through the end of the Johnson administration, thus overseeing each of the critical first crewed missions throughout the Mercury and Gemini programs until days before the launch of the first Apollo mission. He also dealt with the Apollo 1 fire.
Webb directed NASA’s undertaking of the goal set by Kennedy of landing an American on the Moon before the end of the 1960s through the Apollo program. For seven years after Kennedy’s announcement on May 25, 1961, of the goal of a crewed lunar landing, Webb lobbied for support for NASA in Congress, until he left NASA in October 1968. As a longtime Washington insider and with the backing of President Lyndon B. Johnson, he was able to produce continued support and resources for Apollo.

Webb was born in Tally Ho, North Carolina, and graduated from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in 1928. He then earned a law degree from George Washington University in 1930. Webb worked as a lawyer in private practice and then as an administrator in the federal government. He served as Undersecretary of State during the Truman administration.

Webb was appointed Administrator of NASA by President Kennedy in 1961. He was a strong advocate for the space program and played a key role in the Apollo program. Webb retired from NASA in 1968. He died in 1992 at the age of 85.

Webb was a respected leader in the space community and is considered one of the most important figures in the history of NASA. He was awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom in 1969. The James Webb Space Telescope, which was launched in 2021, is named in his honor.
In the vast expanse of space, a new telescope stands poised to revolutionize our understanding of the cosmos. The James Webb Space Telescope, set to launch in the near future, carries a name that honors a remarkable figure in the realm of space exploration: James Webb. In this blog post, we delve into the life and contributions of James Webb, shedding light on the man behind the telescope that bears his name.

The Legacy of James Webb: James Edwin Webb, born on October 7, 1906, in Tally Ho, North Carolina, was an influential American government official and visionary leader in the field of space exploration. He played a pivotal role in shaping NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) and its ambitious missions during a transformative era.
NASA Leadership: Webb’s impact on space exploration began in 1961 when he assumed the role of NASA’s second Administrator. Under his leadership, NASA experienced remarkable progress and achievements during the Mercury, Gemini, and Apollo programs. Webb’s strategic vision and political acumen were instrumental in steering NASA towards one of humanity’s greatest accomplishments—the Moon landing in 1969.
Apollo Program and Moon Landing: Webb’s unwavering support for the Apollo program and his dedication to the mission’s success were key factors in rallying national support and securing the necessary funding for the lunar endeavor. His leadership ensured the Apollo program’s continued momentum, leading to Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin’s historic moonwalk on July 20, 1969.
Expansion of NASA’s Scope: Webb’s tenure as NASA Administrator also saw the expansion of the agency’s scientific research initiatives. Recognizing the potential for discoveries beyond our own planet, Webb championed the exploration of the outer reaches of the solar system and the study of distant galaxies. He believed in the importance of advancing our knowledge of the universe and humanity’s place within it.

Honoring Webb’s Contributions: In recognition of his immense contributions to space exploration, NASA named the next-generation space telescope, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), after him. This cutting-edge observatory is designed to push the boundaries of astronomical research, enabling scientists to observe the universe with unprecedented detail and clarity.
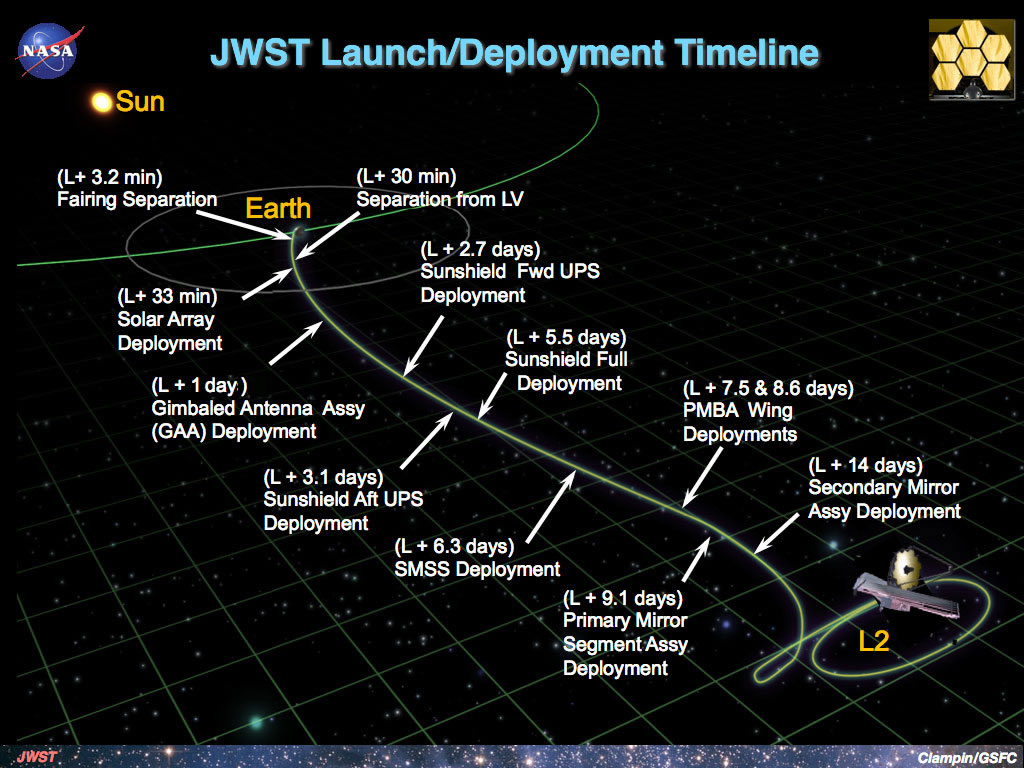
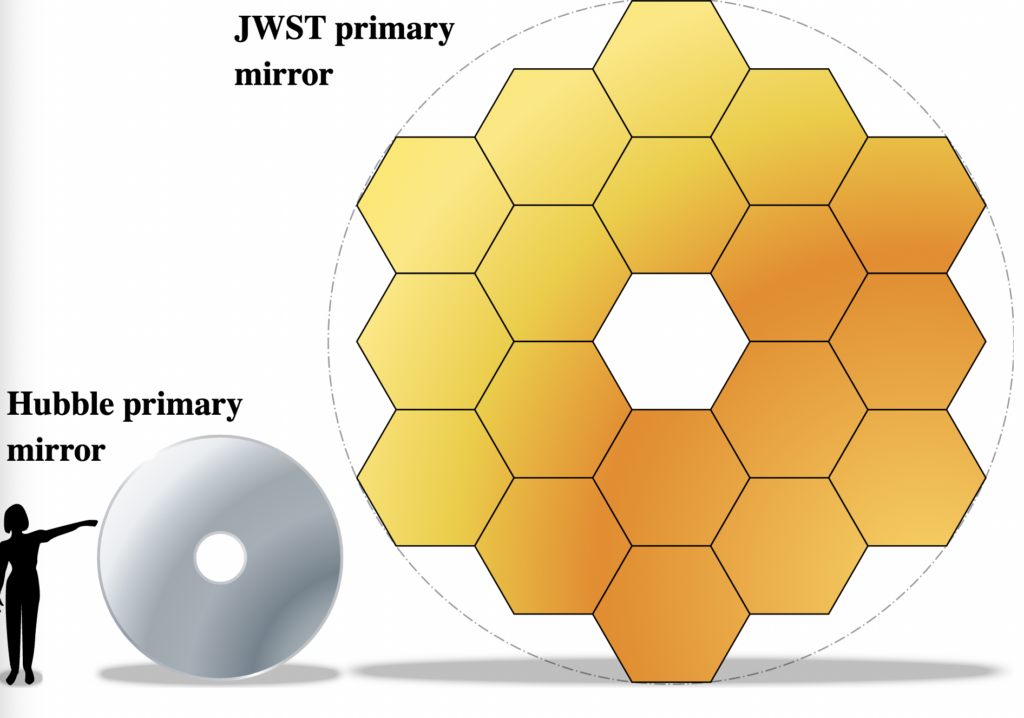
The James Webb Space Telescope: Scheduled to launch soon, the JWST will be a transformative instrument for astronomers worldwide. It will surpass its predecessor, the Hubble Space Telescope, in both sensitivity and capability. Equipped with advanced technologies, the JWST will operate primarily in the infrared part of the electromagnetic spectrum, allowing scientists to explore distant galaxies, observe the formation of stars and planets, and investigate the mysteries of dark matter and dark energy.
James Webb’s dedication, leadership, and vision have left an indelible mark on the field of space exploration. By naming the James Webb Space Telescope after this visionary leader, NASA pays homage to his lasting impact and reinforces its commitment to unraveling the mysteries of the universe. As we eagerly anticipate the launch of the JWST, we can marvel at the achievements of James Webb and eagerly await the discoveries this remarkable telescope will unveil, expanding our knowledge of the cosmos and inspiring future generations of explorers.
- James Webb was the second administrator of NASA, serving from 1961 to 1968. During his tenure, NASA achieved many milestones, including the successful launch of the Apollo 11 mission, which landed the first humans on the moon.
- Webb was a key figure in the Apollo program, and his leadership and expertise were essential to its success.
- Webb was a strong advocate for space exploration, and he believed that space exploration was essential for the United States to maintain its technological and economic leadership.
- Webb was a skilled administrator, and he was able to build a strong team at NASA and to manage the agency effectively.
- Webb was a visionary leader, and he had a clear vision for NASA’s future.
- Webb’s legacy continues to inspire people around the world, and his work at NASA helped to shape the future of space exploration.
Was James Webb cremated on moon?
No, James Webb was not cremated on the moon. He died in 1992 at the age of 85. His ashes were scattered at sea.
There was a proposal to send some of Webb’s ashes to the moon on the Artemis 1 mission, but this plan was ultimately scrapped.
The idea of sending Webb’s ashes to the moon was first proposed by Senator Bill Nelson, who was the former administrator of NASA. Nelson said that he thought it would be a fitting tribute to Webb, who played a key role in the Apollo program.
However, the plan was met with some opposition. Some people argued that it would be disrespectful to send human remains to the moon, while others said that it was simply too expensive.
In the end, the plan was scrapped. NASA said that it would focus on the scientific goals of the Artemis 1 mission, which is the first crewed mission to the moon since 1972.
Despite the fact that Webb’s ashes were not sent to the moon, his legacy will live on. He was a pioneer in space exploration, and his work helped to make the United States a leader in space.